An introductory framework on using artificial intelligence for science and research.
by Yana Stepanyan
Jump to a section
What is AI?
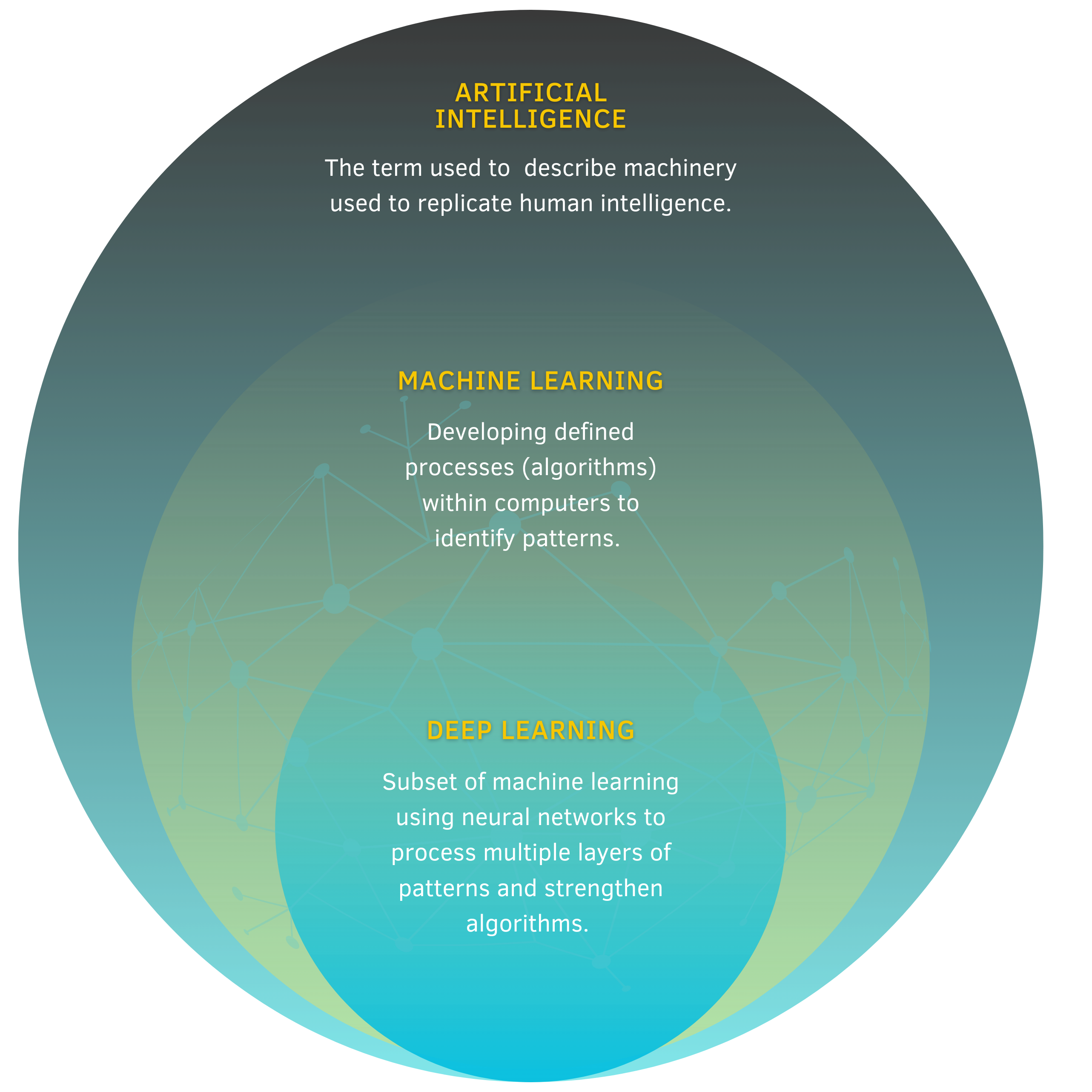
Artificial intelligence (AI) is defined as technology used to simulate human intelligence in order to solve complex problems and algorithms, and build solutions with ease. AI has recently gained popularity amongst various fields such as education, business, art, and particularly, science. Despite it not being a new concept, an idea dating back to the 1920s and emerging in 2012, the release of popular models, such as ChatGPT in 2022, has gained traction and has forever changed how we view innovation.
How does AI Work?
1. Data Input
Gathering data from different sources, such as online sources or pre-existing databases.
2. Data Processing
Raw data is cleaned and organized into a more refined dataset for assessment.
3. Algorithm Selection
Matching the dataset to an algorithm to solve the task presented by the user.

4. Algorithm training
The chosen algorithm learns from the processed data.
5. Model Assessment
Testing the performance of the trained model by assessing its reliability, accuracy, and generalization.
6. Model Application & Refinement
Distributing trained model to other platforms for AI suggestions and assistance. Improving with feedback loop as users increase data input.
Types of AI
Artificial Intelligence comes in many forms. In this section, we’ll explore the different types of AI you can use and some of the most popular platforms and its uses.
Text Generators
These are tools, software, or systems that automatically produce human-like text based on input or prompts. These can provide writing assistance, answer questions, summarize or translate texts.
OpenAI’s newest ChatGPT AI model delivers faster, more accurate, and deeply contextual text generation for users.

Grammarly’s text generator helps users write and refine with tools like brainstorming, outlining, rewording, and more.
Google NotebookLM offers interaction with sources, helping users create summaries and transform complex texts into more simplified formats.
Text to Code
Artificial Intelligence goes beyond traditional text. It can also help users develop and troubleshoot code, making it a powerful tool for data analysis, software development, bioinformatics, and more.
Github Co-Pilot works best for in line coding help and code completions. The coding agent has the ability to make changes given user input and report back, and automate pull requests within Github.
ChatGPT is best for conversational coding help and debugging, where you can describe problems and get clear, working solutions. It’s also ideal for collaborative editing, since it lets you and the AI work together on code or text in real time .
Gemini is best for developers who work directly inside coding tools like VS Code, Github, etc. because it plugs right into those editors and the command line. It’s especially strong for bigger teams or companies, since it can connect with many tools at once, helping automate coding tasks across different projects.
Qodo Gen is designed to make sure your code is solid and reliable. It focuses on automatically writing tests for your code, spotting bugs or weak spots, and helping you follow best practices inside your coding editor.
Choose the tool for you depending on your goal
| I want to: | GitHub Copilot | ChatGPT | Gemini Code | Qodo Gen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Get inline suggestions as I type |  |  |  | |
| Ask for code/explanations |  |  |  | |
| Have the AI check if my code works properly (debug) |  |  |  | |
| Have the AI write a git ‘pull request’ for me |  |  |  | |
| Work across many Integrated Development Environments (X code, VsCode) |  |  |  | |
| Connect AI to apps I already use (Slack, Salesforce, Google Workspace, etc.) |  |  |  |  |
| Reformat code according to best coding practices |  | |||
| Automate multi-step tasks |  |  |  |  |
| Work with these coding languages | Supports a wide range, including Python, R, SQL, C++, Java, JavaScript, MATLAB. | Best with common coding languages like Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, and Go. | Very broad coverage, works with 70+ coding languages. | Strong with popular languages such as Python, Java, JavaScript, and C++. |
| Best Strenghts | Great for speeding up your coding with quick suggestions. | Best for explaining code and helping you debug step by step. | Strong choice if you work in different programming languages. | Best for writing tests, checking code for mistakes, fixing them, and making quality part of the process. |
Speech generation
Text-to-speech gives users the ability to verbally communicate with AI models, offering personalized and real-time support.
- Amazon Alexa: Uses natural language understanding in order to complete real time tasks.
- Gemini API: Utilizes speech to text and text to speech. Also allows users to customize the sound of voice, talking speed, and other configurations.
- Other models: Support personalized podcast creation, lesson planning, voice modifications, and speech-to-text tools.
Multimodal
Various models combine features to create multimodal AI that help with…
- Text Generation
- Coding enhancement
- Voice to text
- Image and digital creations
- Refinement of established data
Comparison of AI Tools for Literature Reviews
Popular tools and what they do
Helps you quickly search through research papers and pull out key points in an organized way.
Finds answers from scientific studies and shows where researchers agree.
Lets you upload a research paper or PDF, then ask questions and get easy to understand explanations.
Works like a smart search engine that chats with you and always shows its sources.
When you might use them
Elicit
Consensus
| When you need a research overview or want to compare many studies easily. |
| When you want a clear, evidence-based answer from published science. |
SciSpace
Perplexity
| When you’re trying to make sense of a long or complicated PDF. |
| When you want quick answers or explanations with links to sources. |
How they work
| Tool | Steps |
| Elicit | You ask a question → it pulls research papers → shows results in tables or summaries |
| Consensus | You type a question → it scans scientific studies → gives an answer with a “consensus” score |
| SciSpace | You upload a PDF → ask questions about it → it explains sections in plain English |
| Perplexity | You ask anything → it finds answers online → gives short explanations with clickable sources |
AI for Science
This section highlights how artificial intelligence is advancing scientific research. By applying powerful models to biology, genetics, and chemistry, AI can help scientists with predicting protein structures, analyzing DNA sequences, and integrating biological data with natural language for faster insights.

ChatNT
ChatNT analyzes genetic sequences by reading DNA, RNA, and proteins like language and explaining the results in clear words.